Causal Cartographer: From Mapping to Reasoning Over Counterfactual Worlds

Overview
We introduce the Causal Cartographer, a retrieval-augmented system for causal extraction and causal knowledge representation, and a methodology for provably estimating real-world counterfactuals. We show that causal-guided step-by-step LRMs can achieve competitive performance while greatly reducing LLMs’ context and output length, decreasing inference cost up to 70%.
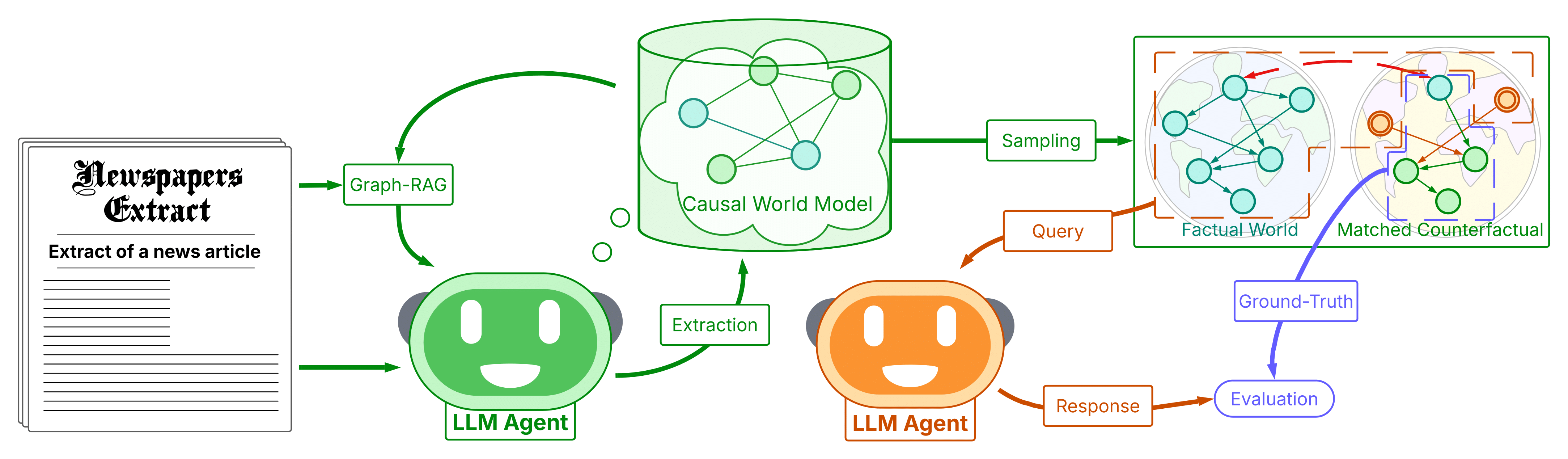
The Causal Cartographer (figure above) is the resulting instantiation of the idea developed in our Counterfactual Causal Inference in Natural Language project, which aims to build automatic systems able to parse texts for causal structures and take advantage of them to conduct robust reasoning, specifically reasoning abut causes and effects, build counterfactual scenarios, and evaluate the impact of interventions in an environment.
Causal Cartographer
The Causal Cartographer is composed of two modules: a retrieval and a reasoner agents. The extractor is a retrieval-augmented system that extracts causal realtionships from natural language texts and summarizes it into a causal network. The reasoner is a step-by-step Markovian reasoning system that uses the extracted causal knowledge to reason: it iteratively deduces effects from their causes to make predictions about long-term effects, and uses causal interventions to estimate counterfactuals.
CausalWorld
CausalWorld is the intermediate causal knowledge mapped by the cartographer, a large-scale causal knowledge graph of the real world. An overview of CausalWorld is shown at the top of the page and an example of causal chain is shown below.
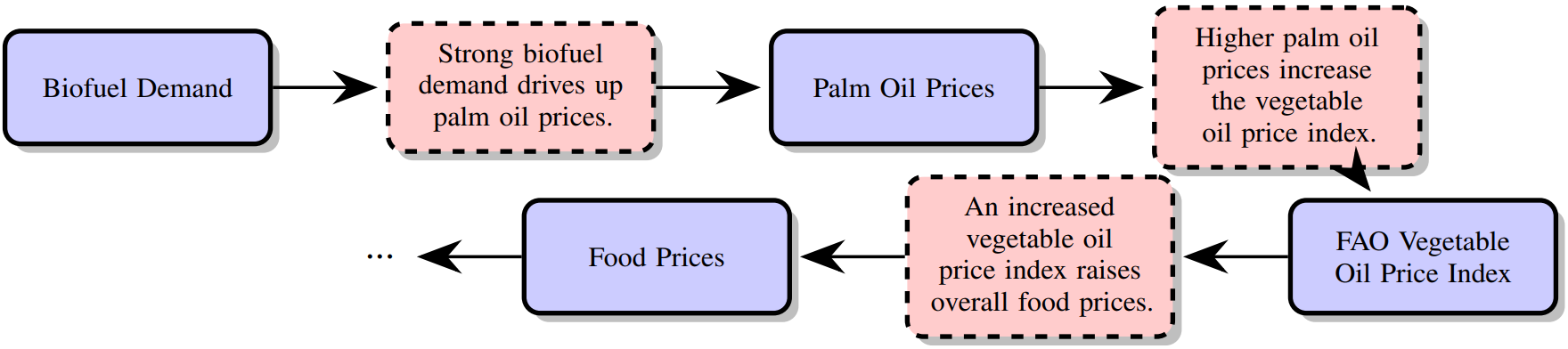
In addition to representing causal knowledge, CausalWorld can be used to estimate real-world counterfactuals. Information collected from various sources can be mapped as different instantiations of a same variable (e.g. the biofuel demand can differ between different countries, or the same country at different times). Given sufficient information, alternative worlds can be constructed, counterfactuals of each other, representing of the same variables would evolve under different conditions. The Causal Cartographer can then estimate the effects of interventions in these worlds, and thus estimate real-world counterfactuals.
Key Takeaways
Causal Extraction: We propose a retrieval-augmented system for causal extraction and representation, which can be used to build large-scale causal knowledge graphs of the real world.
Causal World Models: We build CausalWorld, a large-scale causal knowledge graph of the real world, which can be used to estimate real-world counterfactuals.
Counterfactual Reasoning: We propose a step-by-step reasoning system that can estimate real-world counterfactuals by iteratively deducing effects from their causes and using causal interventions.
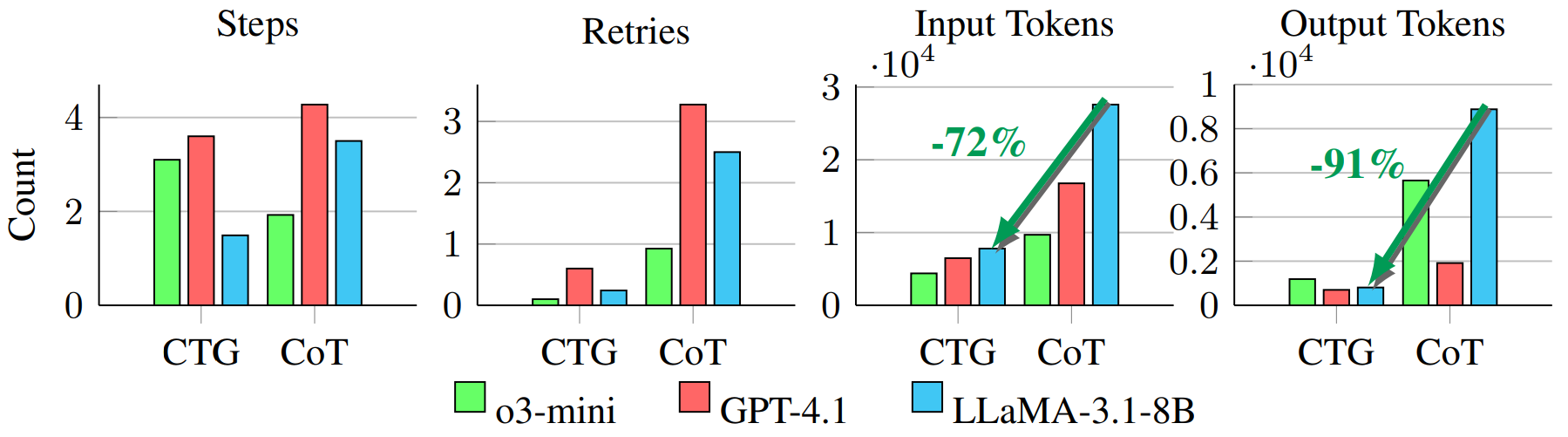
Experiments: We show that the Causal Cartographer (CTG) can achieve competitive performance on real-world counterfactual reasoning tasks (extracted from CausalWorld) while demonstrating increasing robustness. Numerical results are available in the paper. It is also much more efficient. Compared with chain-of-thought, it greatly reduce LLMs’ context and output length, decreasing inference cost up to 70%.
Future Directions
The Causal Cartographer is an initial step towards building systems of higher cognition that can reason about cause and effect in the wild: recover and test causal relationships, estimate the effect of an intervention (e.g. a policy change), and build counterfactual scenarios to evaluate the impact of these interventions while grounding and explaining their reasoning with causal knowledge. We hope that this work can guide the research community towards robust and safe AI systems that can reason about the real world and make informed decisions based on causal knowledge.